Flight requires two things: thrust and lift.
Thrust
Thrust is the forward motion provided by a propeller or jet engine.
Lift on an aeroplane wing
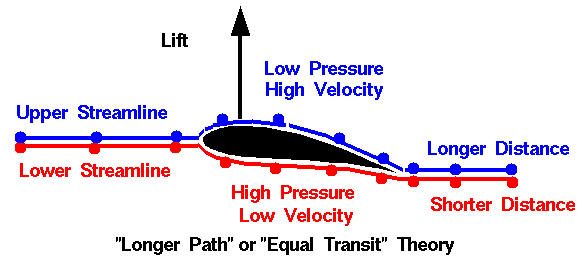
The shape of the aeroplane wing is peculiar. Its upper surface is
more curved than its lower surface and its leading edge is thicker than its trailing edge. As an aeroplane moves forward, the air blown in the form of stream lines over the wings of aeroplane is shown below.
As the upper surface of wing is more curved than its lower surface, therefore, the speed of air above the wings two is larger than the speed of the air below the wings. According to Bernoulli’s theorem, the pressure above the wings becomes less than that the pressure
below the wings. Due to this difference of pressure on the two sides of the wings, a vertical lift acts on the aeroplane. When this lift is sufficient to overcome the gravity pull on the aeroplane, the aeroplane is lifted up.
Drag
Two forces work against flight: drag and gravity.
A wing has to be designed not only to produce lift, but also to minimize the friction with passing air, which causes drag.
Every airplane has a specific takeoff speed, where lift overcomes gravity. That critical speed changes based on how much weight a particular flight packs. The planes propeller or jet engine, meanwhile, has to work to provide enough thrust to overcome drag.
Pilots can make minor adjustments to the wing flaps, effectively changing the wing's angle into the wind. A more tilted wing allows more lift to be created at a lower speed.

No comments:
Post a Comment